Legal Remedies Available for Victims of Cyber Stalking and Cyber Harassment
In today’s digital age, our lives are deeply connected through smartphones, social media, and online platforms. While this connectivity has opened doors to countless opportunities, it has also given rise to disturbing online behaviors such as cyber stalking and cyber harassment. These forms of digital abuse go beyond ordinary disagreements on the internet — they often involve repeated, unwanted attention, monitoring, intimidation, or threats that can cause serious emotional and psychological harm.
Broadly speaking, cyberstalking and harassment refer to the persistent misuse of digital technologies to target individuals. Where cyber harassment may include abusive messages, defamatory posts, or threats, cyber stalking typically involves continuous tracking, monitoring, or attempts to control someone’s online presence. Both are recognized as forms of cyber harassment crime, and fall under the growing category of harassment in cyber crime cases being reported across India.
Recent trends highlight the alarming scale of this issue. According to data from the Jaipur Cyber Support Centre, cases of online abuse have risen sharply in the past few years, with nearly 30% of reported victims being women. This mirrors a national trend where young internet users, especially women and children, face higher risks of becoming targets of cyber stalking or harassment.
The rise in such cases underscores why legal remedies are essential. Victims often feel trapped, vulnerable, and silenced. Legal frameworks not only provide mechanisms to address cyber harassment crimes, but also act as a deterrent to offenders. Understanding the laws and remedies available empowers individuals to take timely action, protect themselves, and seek justice against cyberstalking and harassment in all its forms.

Understanding Cyber Stalking & Cyber Harassment
The rise of digital communication has blurred the lines between harmless online interactions and harmful behavior. While the two terms are often used interchangeably, there are key distinctions:
- Cyber stalking – refers to a pattern of continuous, unwanted digital surveillance or contact. It often includes monitoring social media activity, sending persistent messages, or using technology to track someone’s online movements. Many experts emphasize that the cyber stalking definition in law highlights this repetitive and intrusive nature.
- Cyber harassment – on the other hand, covers a broader range of abusive behavior online — from sending threats or insults to spreading false information. Unlike cyber stalking crimes, harassment may not always involve long-term monitoring, but it can still be extremely damaging.
Other related behaviors include:
- Online bullying – targeted humiliation or threats, especially among teenagers.
- Doxxing – publishing private or personal details without consent.
- Revenge porn – sharing intimate images/videos to shame or control a victim.
Together, these behaviors fall under the scope of laws about online harassment, as India strengthens its digital safety framework.
Common Forms of Abuse
Victims of cyber stalking and cyber harassment often face a range of actions that are designed to intimidate or humiliate them. Some of the most common include:
- Repeated, unwanted messages or calls
- Constant monitoring of social media profiles
- Impersonation through fake accounts
- Posting obscene or defamatory content
- Identity theft to damage reputation or cause financial harm
- Circulation of morphed photos or private videos
Such acts are treated as serious cyber stalking crimes under evolving Indian laws.
How the Law Sees It: Direct vs. Indirect Abuse
Indian legal frameworks recognize that digital abuse can be both direct and indirect:
- Direct abuse includes explicit threats, obscene content, or relentless messages.
- Indirect abuse may involve spreading rumors, impersonating the victim online, or creating fake accounts to harass.
This is where internet stalking laws, the online harassment act, and other provisions under the online harassment law come into play. They acknowledge that both visible attacks and subtle, hidden forms of intimidation qualify as punishable offenses.
By framing these acts within a legal perspective, India seeks to provide clear protection against cyber stalking and cyber harassment, ensuring victims have defined remedies when facing digital abuse.
Understanding the Offences Under Indian Law
With the rise of digital abuse, cyber stalking and cyber harassment laws have become critical in India. Both the Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act) and the Indian Penal Code (IPC) — along with the newly enacted Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS, 2023) — lay down specific provisions to address online abuse, identity theft, and social media harassment laws. Understanding these offences helps victims know where the law stands on cyber stalking and related crimes.

Offences under the Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
The cyber stalking law in India is strongly supported by the IT Act, which specifically deals with crimes committed through digital platforms. Key sections include:
- Section 66C – Identity Theft: Using someone else’s digital identity (passwords, electronic signatures, or personal details) is a punishable offence. This is especially relevant in social media harassment laws where fake profiles are created to defame or harass.
- Section 66D – Impersonation: Fraudulently impersonating another person online for cheating or harassment can lead to imprisonment of up to 3 years and fines.
- Section 66E – Violation of Privacy / Voyeurism: Capturing, publishing, or transmitting private images without consent falls under this section, directly protecting victims of cyber harassment laws.
- Sections 67 & 67A – Publication or Transmission of Obscene Content: Sharing obscene or sexually explicit content online is a serious offence. Penalties may include imprisonment ranging from 3 to 7 years and heavy fines.
Together, these provisions strengthen cyber stalking laws in India, ensuring accountability for digital intrusions.
Offences under IPC and Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS, 2023)
While the IT Act is technology-focused, the Indian Penal Code and the new Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) add a broader criminal law perspective to cyber stalking laws and harassment-related cases.
- Section 354D IPC – Stalking: This section directly addresses cyber stalking law by criminalizing repeated online contact, monitoring, or following a person electronically.
- First offence: Up to 3 years imprisonment and fine.
- Subsequent offence: Up to 5 years imprisonment and fine.
- Section 354A IPC – Sexual Harassment: Covers unwelcome sexually colored remarks, messages, or advances made online.
- Section 509 IPC – Insulting the Modesty of a Woman: Protects women from obscene messages or online comments.
- Sections 499 & 500 IPC – Defamation: Posting defamatory content online to harm reputation comes under this.
- Sections 503, 506 & 507 IPC – Criminal Intimidation: Threats or blackmail through digital platforms are punishable.
- BNS, 2023 (New Provisions): The recently introduced Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita has updated cyber stalking laws in India, covering stalking, voyeurism, and online abuse with stricter punishments to reflect modern realities of digital crime.
Why These Laws Matter
- They provide a legal framework for addressing harassment on digital platforms.
- They ensure both preventive and punitive measures against offenders.
- They align with the growing need for social media harassment laws, given the increase in cases across Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp.
In short, the combined approach of the IT Act, IPC, and BNS reinforces India’s cyber harassment laws, giving victims more avenues for justice under cyber stalking laws in India. For a deeper dive into India’s cyber laws and how they shape online safety, you can explore our detailed blog on Indias Cyber Laws.
Available Legal Remedies for Victims of Cyber Stalking & Harassment
Victims of cyber stalking and harassment often feel powerless, but Indian law provides several avenues to seek redressal. From filing a cyber-crime complaint procedure to pursuing civil remedies, the legal system is designed to help protect individuals from online abuse and harassment. While these steps are not legal advice, they serve as a guide to understanding the procedure for cyber-crime complaint and possible remedies.

Criminal Remedies
When facing cyber stalking or cyber harassment, the first and most effective response is to approach law enforcement. Victims can use multiple channels:
- Filing an FIR: An FIR can be lodged at the nearest police station or directly with the cyber-crime cell in the victim’s city. Many metropolitan cities now have specialized cyber cells equipped to handle cases of cyber stalking and other digital crimes.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal: Complaints can also be filed online via the official government portal (cybercrime.gov.in). This online mechanism simplifies the procedure for cyber-crime complaint, especially for victims who may hesitate to approach the police in person.
- Use of IT Act & IPC/BNS Together: Often, a single act of cyber harassment can fall under both the Information Technology Act and the Indian Penal Code/Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS). For instance, a case of impersonation (IT Act, Section 66D) may also amount to cheating under IPC provisions. Law enforcement agencies can apply both sets of laws to ensure stronger protection.
Civil and Interim Reliefs
In addition to criminal remedies, victims of cyber stalking and harassment can also seek civil or interim protections to safeguard themselves. These remedies are particularly useful when the perpetrator is known to the victim or continues to cause emotional distress.
- Protection Orders under PWDVA, 2005: If the offender is a domestic partner, the victim can seek protection orders under the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act. This extends the scope of cyber harassment protection within intimate relationships.
- Restraining Orders & Cease-and-Desist Notices: Victims may approach an online harassment lawyer to file for restraining orders in court. A lawyer can also issue a cease-and-desist letter to warn the perpetrator against continued cyber stalking or digital abuse.
- Civil Suits for Defamation or Privacy Invasion: Victims may also pursue damages for defamation, violation of privacy, or mental anguish caused by cyber harassment. This requires the assistance of a cyber-harassment lawyer, who can guide the victim through civil litigation processes.
Ultimately, understanding the cyber-crime complaint procedure empowers victims of cyber stalking and cyber harassment to take the right steps towards safety and justice.
Practical Steps for Victims of Cyber Stalking or Cyber Harassment
Facing cyber stalking or cyber harassment can be overwhelming, but victims should know that there are clear and practical steps to safeguard themselves and pursue justice. While the law provides for cyberstalking punishment and other penalties, the journey begins with timely action by the victim.
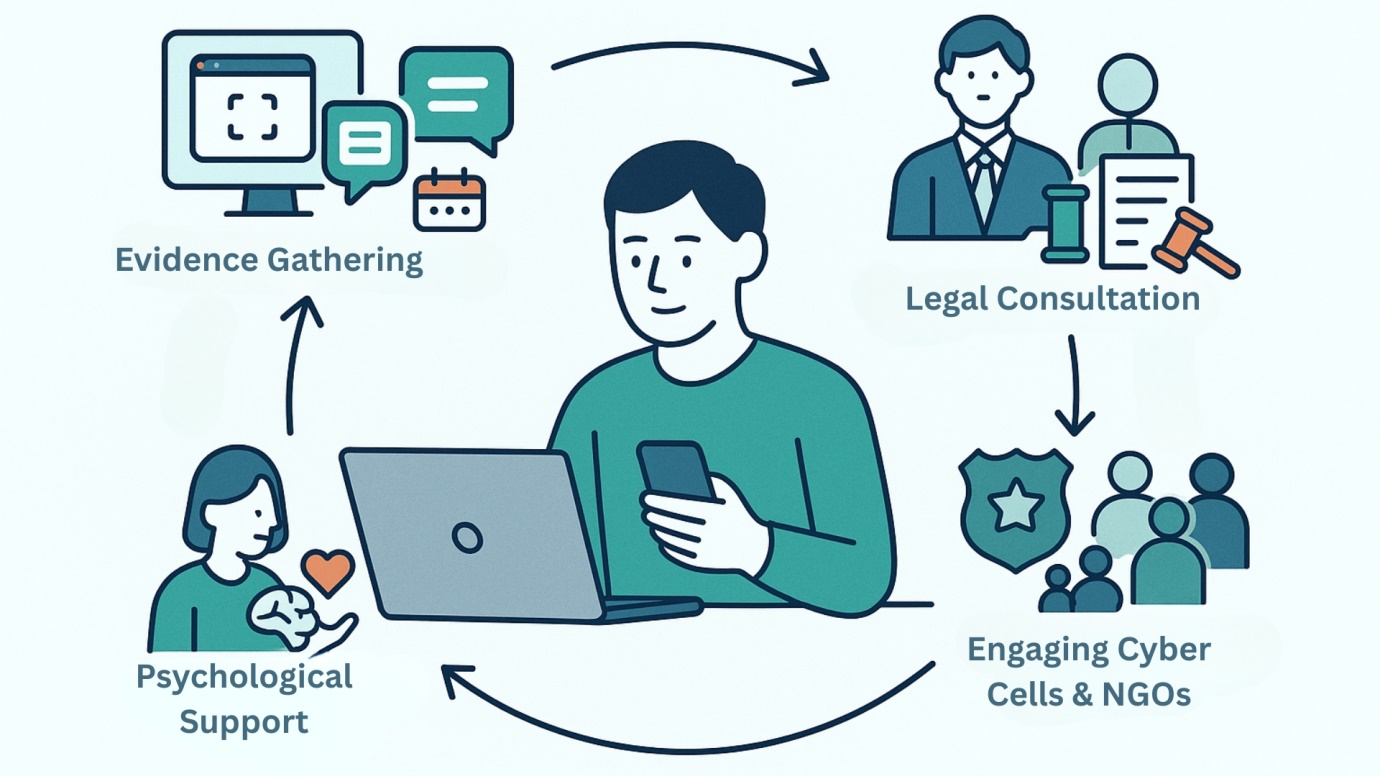
Evidence Gathering
Before initiating any complaint, it is crucial to collect strong evidence of cyber harassment or cyberstalking. Since most offences occur in digital spaces, evidence must be preserved carefully:
- Take Screenshots: Preserve offensive posts, messages, or emails.
- Save Chat Logs & Emails: Do not delete abusive conversations or emails.
- Preserve Metadata: Technical details such as timestamps and IP logs can strengthen a complaint.
- Document Patterns: If the abuse is repetitive, maintain a timeline to show persistent conduct.
Such evidence becomes the backbone of any police complaint and plays a role in ensuring that punishment for cyberstalking is enforced.
Legal Consultation
Victims should not navigate the system alone. Consulting a cybercrime lawyer can help:
- Assess whether the conduct qualifies as cyber harassment or cyber stalking under law.
- Identify applicable provisions, including cyber stalking punishment in India under the IPC/BNS and IT Act.
- Draft legal notices, file FIRs, and provide representation in court if required.
By engaging a professional, victims increase their chances of holding perpetrators accountable and ensuring stricter cyberstalking punishment.
Engaging Cyber Cells & NGOs
- Cyber Cells: Almost every state and major city has a dedicated cyber-crime cell. Victims of cyber stalking can approach them directly or file complaints online.
- NGOs & Support Groups: Several NGOs in India assist victims of cyber harassment by providing legal guidance, counselling, and advocacy.
Such support structures ensure that the cyber stalking punishment in India is not just a legal provision but also a practical reality when perpetrators are caught.
Psychological Support
Beyond legal action, the emotional impact of cyber harassment and cyber stalking should not be ignored.
- Victims can seek therapy or counselling to cope with stress and trauma.
- Support from family, friends, or peer groups can help restore confidence.
- Specialized mental health professionals now recognize online abuse as a significant factor in psychological harm.
Seeking mental well-being is as important as ensuring legal punishment for cyberstalking.
These steps, when followed, not only strengthen the case but also ensure that offenders face the rightful cyber stalking punishment in India as laid down by law.
Evidence & Cyber Forensics Essentials
When it comes to cyber stalking or cyber harassment, the strength of the victim’s case depends heavily on the quality of evidence collected. In the digital world, everything leaves a trace, and understanding how to preserve and present that evidence is crucial. This is where cyber-crime forensics and the proper use of legal procedures come into play.

Importance of Preserving Digital Evidence
Victims must act proactively to secure evidence in cyber-crime cases, as tampering or delay can weaken their complaint. Some important practices include:
- Screenshots & Recordings: Capture abusive messages, social media posts, and emails related to cyber stalking or cyber harassment.
- Chat Logs & Call Records: Store complete communication histories without editing or deleting them.
- Metadata Preservation: Metadata (time stamps, sender IP, geolocation data) is often more critical than the message itself.
- Email & Server Logs: Retaining backend data can help investigators trace the origin of threats or impersonation.
Such documented evidence often plays a decisive role in cyberstalking court cases, where the victim must establish a clear trail of abuse.
Section 65B of the Indian Evidence Act
In India, electronic evidence is admissible in court only if it is properly certified under Section 65B of the Indian Evidence Act. This certification ensures that digital files—screenshots, emails, or video recordings—are treated as genuine and tamper-proof.
Without this certificate, crucial evidence in cyber-crime cases may not hold up in legal proceedings. Hence, victims and lawyers must work closely with investigators and digital experts to ensure compliance with this requirement.
Role of Cyber Forensics in Legal Strategy
Cyber crime and forensics play a pivotal role in building a strong legal case. Forensic experts help in:
- Tracing IP Addresses: Identifying the origin of threatening or abusive communications.
- Recovering Deleted Data: Even erased messages or files can be retrieved through cyber crime forensics
- Authenticating Evidence: Establishing the originality of digital records to counter claims of fabrication.
- Expert Testimony: In many cyberstalking court cases, forensic experts provide testimony to validate digital evidence.
By integrating cyber crime and forensics into their legal strategy, victims can strengthen their complaints and ensure that perpetrators of cyber stalking or cyber harassment face accountability.
The fight against cyber harassment and cyber stalking is not only about filing complaints but also about presenting reliable evidence in cyber-crime cases. With proper preservation of digital proof, certification under Section 65B, and the expertise of cyber crime forensics, victims stand a stronger chance in cyberstalking court cases.
FAQs
A. Cyber stalking usually involves persistent monitoring, following, or threatening someone online, while cyber harassment can include abusive messages, defamation, or obscene posts. Both are recognized as harassment in cyber crime under Indian law.
A. Typical cyber stalking crimes include repeated unwanted messages, identity theft, impersonation, fake profiles, doxxing, and obscene content posted on social media.
A. Yes, India has cyberstalking laws under both the Information Technology Act, 2000 and the Indian Penal Code (IPC). These provisions address identity theft, voyeurism, obscene content, and stalking offences.
A. The cyber stalking punishment in India can include imprisonment, fines, or both, depending on the severity of the offence. The punishment for cyberstalking under IPC Section 354D may extend up to 3 years for a first offence and 5 years for subsequent offences.
A. Yes, victims of cyber harassment crime may seek restraining orders, cease-and-desist notices, or protection orders through civil remedies, especially under laws like the PWDVA if the perpetrator is a domestic partner.
A. Cyber crime forensics is crucial in gathering evidence in cyber crime cases. Experts analyze metadata, chat logs, and device footprints, which are often used in cyberstalking court cases to prove harassment.
A. Section 65B certifies electronic records such as screenshots, call logs, or messages. This certification is necessary for using digital evidence in cyber harassment or cyberstalking law cases in court.
A. Yes, social media harassment laws cover impersonation and fake profiles created to harm someone’s reputation or privacy. Such acts fall under cyber stalking and harassment provisions in India. To know more about how fake accounts and online defamation are handled legally, check out our detailed blog on Social Media and Cyber Defamation.
A. Absolutely. Victims can pursue both criminal remedies under the IT Act and IPC, while also filing civil suits for defamation, privacy invasion, or emotional distress caused by cyber harassment.
A. Yes, laws about online harassment include IPC sections on defamation, criminal intimidation, and sexual harassment, as well as IT Act provisions related to obscene or offensive online content.
Conclusion
The rise of cyber stalking and cyber harassment in today’s digital age highlights the urgent need for awareness, vigilance, and timely action. Victims often hesitate to report incidents due to fear, stigma, or lack of information, but legal mechanisms exist to provide protection and justice. From registering complaints under the procedure for cyber crime complaint to seeking guidance from a cyber harassment lawyer or an online harassment lawyer, multiple avenues are available to ensure that offenders are held accountable.

Why Timely Action Matters
- Preserving Evidence: Digital evidence can be lost, deleted, or tampered with, making early reporting critical in cyber harassment crime cases.
- Preventing Escalation: Unchecked cyberstalking and harassment often escalate from online threats to offline dangers.
- Stronger Legal Grounds: Prompt filing of a cyber crime complaint procedure ensures that victims can use both IT Act and IPC/BNS provisions effectively.
Building Awareness and Support
Fighting harassment in cyber crime is not just about punishment; it is also about creating safer online spaces. This requires:
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating individuals about cyberstalking laws and cyber harassment laws so they know their rights.
- Professional Assistance: Victims should not hesitate to reach out to a cyber harassment lawyer or legal aid groups for guidance.
- Community and NGO Support: Specialized organizations provide counselling, technical support, and legal help for survivors of cyberstalking.
While cyberstalking and cyber harassment continue to be growing threats, legal remedies, technological safeguards, and support systems are in place. The most important step is to take action without delay—whether that means collecting evidence, filing a complaint, or consulting professionals.
A society informed about cyberstalking crimes and equipped with the right resources can ensure that victims receive protection, perpetrators face consequences, and the digital space becomes safer for all.
For more insights into related legal topics or to understand how professional legal support works, you may also explore our Home Page for general information.
Disclaimer:
This blog is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It should not be taken as legal advice or relied upon as such. Cases of cyberstalking and cyber harassment are highly sensitive and often vary based on individual circumstances, which may affect the legal remedies available.
If you or someone you know is facing such challenges, it is advisable to seek guidance from a qualified cyber harassment lawyer or legal professional. For safe and confidential support, you may also consider reaching out to trusted legal platforms such as Adlegal.



